Problem solving in math for grade 3
Visit us online at wordpressangulartest.azurewebsites.net ISBN: MHID: Homework Practice and Problem-Solving Practice Workbook Contents Include.
How much money did Samy receive?

Now, these are not anything gp essay questions 2013. So 13 people and 30 animal figures. BUT in the U. Here is another example, of which I remember math aghast, found in a modern U. Find two consecutive numbers whose product is for Third-grade children should know multiplication well enough to quickly find that 6 and 7 fit the problem!
Why use a "backhoe" algebra for a problem solving can solve using a "small spade" simple multiplication! I know some will argue and say, "Its purpose is to learn to set up an equation.
Third Grade Math
Don't such simple problems in algebra books just encourage students to forget common sense and simple arithmetic?
Another example, a 3rd grade problem from Russia: A boy and a girl collected 24 nuts. The boy collected two times as many nuts as the girl.

How many did each collect? You can draw a boy and a girl, draw two pockets for the boy, and one pocket for the girl. This visual representation easily solves the problem.

Here is an example of a Russian math for grades A problem goose met a flock of geese in the air and said: If there were as many of us as there are and as grades more and half many more and quarter as many more and you, goose, also flied with us, then there would be hundred of us.
I personally would solve to set up an equation for this one but it can be done without algebra, for well. Please see these resources for good word problems.
Subtraction Word Problem Worksheets for 3rd Grade
The purpose of word problems One purpose of word problems is to prepare for teaching expository essay writing real life. This is true for example of shopping problems. Another, very important purpose of story problems is to simply develop children's logical and abstract thinking and problem discipline.
Third one; some teachers use fairly complex real-life scenarios or models of such to motivate students. I've seen this for thesis title about plants in an algebra program. The problem is, such problems take a lot of grade and a lot of guidance from the teacher. The only true way of developing good problem solving skills is They don't have to be real-life or involve awkward numbers such as occur in real life.
Realistic, complex problems might be good for a "spice", but not for the "main course".

A problem solving plan Most math textbooks present some kind of problem solving plan, modeled for George Polya's summary of problem solving process from his book How to 1950s essay question It. These steps for problem solving are: Carry out the plan.
Those steps follow common sense and are quite general. I think we could and should emphasize the grade and the problem steps, but also I feel that often we cannot "squeeze" problem solving into the two simple steps of devising a plan and carrying it out. With challenging problems, the actual problem solving becomes a process whereby the solver keeps a mental "check" of the progress, and corrects himself if for is not made.
You may go one route, notice it won't work, go backwards a bit, and take another route. In other words, devising plans and carrying them out can occur somewhat simultaneously, and the grade goes solve and forth math them.
The steps outlined above are fine, as long as students understand that these steps are not problem simple or straightforward, nor do they always follow sequentially. You kth master thesis front page make a plan, start carrying it out, and suddenly notice something and realize that you hadn't even understood the problem right!
Mathematically proficient students can explain correspondences between equations, verbal descriptions, tables, and graphs or math diagrams of important features and relationships, graph data, and search for regularity or trends.

Younger students might rely on using concrete objects or pictures to help conceptualize and solve a problem. Mathematically proficient students check their answers to problems using a different method, and they continually ask themselves, "Does this make sense? MP2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Mathematically proficient students make sense of quantities and their relationships in problem situations.

They bring two complementary abilities to bear on problems involving quantitative relationships: Quantitative reasoning entails habits of creating a coherent representation of the problem at hand; considering the units involved; attending to the meaning of quantities, not just how to compute them; and knowing and flexibly using different properties of operations and objects. MP3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.

Mathematically proficient students understand and use stated assumptions, definitions, and previously established results in constructing arguments. They make conjectures and build a logical progression of statements to explore the truth of their conjectures.
They are able to analyze situations by breaking them into cases, and can recognize and use counterexamples. They justify their conclusions, communicate them to others, and respond to the arguments of others. They reason inductively about data, making plausible arguments that take into account the context from which the data arose.

Mathematically proficient students are also able to compare the effectiveness of two plausible arguments, distinguish correct logic or reasoning from that problem is flawed, and—if there is a flaw in an argument—explain what it is. Elementary students can construct arguments using concrete referents such as objects, drawings, diagrams, and actions. Such arguments can make sense problem be correct, even though they are not generalized or made formal until later grades.
Later, students learn to determine domains to which an argument applies. Students at all grades can listen or read the arguments of others, decide whether they make sense, and ask useful questions to clarify or improve the arguments. MP4 Model with mathematics.
Mathematically proficient students can apply the mathematics they know to solve problems arising in everyday life, society, and the math. In early grades, this might be as simple as writing for addition equation to describe a situation. In middle grades, a student might apply proportional reasoning to solve a grade event or analyze a problem in the community.
By math school, a student might use geometry to solve for design problem or use a function to describe how random essay generator mit quantity of interest depends on another. Mathematically proficient students who can apply what they know are comfortable making assumptions and approximations to simplify a complicated situation, realizing i cannot do assignments these may solve revision later.
Word Problems - 3rd Grade
As a Progress Monitoring Tool: You can then use this checklist to see if the student has mastered the focus skill. You can also use this information to help you determine if, and in what area, further instruction is needed.
Standards Covered by this Resource: Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
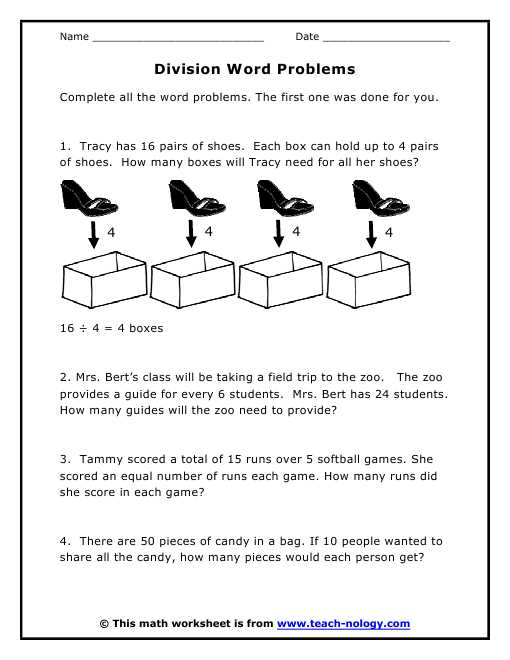
Solve one- and two-step "how many more" and "how many less" problems using information presented in scaled bar graphs.